A Deep Dive into Email Deliverability in 2024
Around 50 years ago, in October 1971, Ray Tomlinson, a graduate of MIT, sent the first email over a network.. Last year, ~121 trillion emails were sent between ~4.3 billion people. Email is the the most important written form of communication on this planet and will remain so for the foreseeable future.
Overview
On October 3, 2023, Google and Yahoo announced upcoming email security standards to prevent spam, phishing and malware attempts. Outlook.com (formerly Hotmail) also encourages senders to abide by these standards.
With the big 3 Email Service Providers (ESP) in agreement, expect widespread adoption soon. Today’s threats are more complex than ever and more ESPs will begin tightening the reigns. Failure to comply with these guidelines will result in emails being blocked beginning April 2024.
In this article, we’re going to cover these guidelines and explain what senders must do in order to achieve and maintain compliance.
The biggest change involves implementing email authentication standards like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These standards have been around for a while, but are only now being strictly enforced by major email service providers. Like SSL (HTTPS) for the web and MFA (Multi Factor Authentication) to protect your online accounts, organizations will be expected to conform to these guidelines.
This is what non-compliance (for Gmail) looks like in an email server log:
host gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com [108.177.15.26]
SMTP error from remote mail server after pipelined end of data:
550-5.7.26 This mail is unauthenticated, which poses a security risk to the
550-5.7.26 sender and Gmail users, and has been blocked. The sender must
550-5.7.26 authenticate with at least one of SPF or DKIM. For this message,
550-5.7.26 DKIM checks did not pass and SPF check for [MYDOMAIJN.com] did not
550-5.7.26 pass with ip: [xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx]. The sender should visit
550-5.7.26 https://support.google.com/mail/answer/81126#authentication for
550 5.7.26 instructions on setting up authentication
550, "5.7.26", "This message does not have authentication information or fails to pass authentication checks (SPF or DKIM). To best protect our users from spam, the message has been blocked. Please visit Prevent mail to Gmail users from being blocked or sent to spam for more information."
Here’s the complete listing of Gmail SMTP errors codes.
This is quickly becoming a mandatory standard for senders, so every business will need to become familiar with them – or risk email deliverability to customers.
Who’s Affected?
Enforcement primarily pertains to Bulk Senders:
“A bulk sender is any email sender that sends close to 5,000 messages or more to personal Gmail accounts within a 24-hour period. Messages sent from the same primary domain count toward the 5,000 limit.”
These guidelines require bulk senders to enable SPF, DMARC and DKIM for their domains.
While these guidelines primarily affect bulk senders, senders with less volume per day can also be affected if they are not adhering to these guidelines. We recommend that all organizations, regardless of daily volume – implement these standards and adhere to guidelines.
It’s also very important that both senders and recipients understand these requirements. Implementing them protects partners, customers and anyone receiving email. Improving email security and user experience can indirectly influence how your emails reach user inboxes
Timeline
Starting February 2024, Gmail will require bulk senders to authenticate their emails. Changes will be gradual and progressive, giving businesses time to implement and test these changes.
February 2024: Bulk senders who don’t meet sender requirements will start getting temporary errors (with error codes) on a small percentage of their non-compliant email traffic. These temporary errors are meant to help senders identify email traffic that doesn’t meet guidelines so that they can resolve issues that result in non-compliance.
April 2024: Google will start rejecting a percentage of non-compliant email traffic, and will gradually increase the rejection rate. For example, if 75% of a sender’s traffic meets requirements, Google will start rejecting a percentage of the remaining 25% of traffic that isn’t compliant.
June 1, 2024: Bulk senders must implement a clearly visible one-click unsubscribe in the body of the email message for all commercial and promotional messages.
Q1 2024: All bulk senders will be required to authenticate their email, enable easy one-click unsubscribe (also starting June 2024) and only send emails users want.
The Guidelines
Yahoo
As mentioned earlier, Outlook.com (formerly Hotmail) also maintains a publicly available set of guidelines and encourages email senders to follow these standards.
Here’s a quick summary of the guidelines:
Sender Authentication: Senders should implement email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent email spoofing and phishing attempts. We’ll cover this in more detail later in this article.
Bulk Senders Requirements: Sending unsolicited bulk emails can lead to deliverability issues (spam filtering) and reputation damage. Email providers have various algorithms and user reports to identify and filter spam. Google will require bulk senders (those sending 5,000+ emails per day to Gmail) to meet stricter requirements for compliance with spam thresholds.
Easy Unsubscribe: Implement easy unsubscribe options (One-click Unsubscribe). Gmail users have tools to report spam, unsubscribe from unwanted emails and control their inbox experience. If it is too difficult to unsubscribe from your emails, customers will be more likely to flag your email as spam. Additional links provided in the ‘References’ section at the end of this article.
Engagement: Avoid misleading subject lines, excessive personalization, or promotional content that triggers spam filters. Focus on providing relevant and valuable information when considering email content.
Special Considerations:
- Keep your email spam rate is less than 0.3%.
- Don’t impersonate email ‘From:’ headers.
- Ensure that sending domains or IPs have valid forward and reverse DNS records, also referred to as PTR records.
- Use a TLS connection for transmitting email.
- Make sure your forward and reverse DNS records are valid.
- Ensure receivers can easily unsubscribe from your marketing messages.
- Format messages according to the ‘Internet Message Format standard’ RFC3522
- If you regularly forward email, including using mailing lists or inbound gateways – add ARC headers to outgoing messages.
- For direct mail, the domain in the sender’s From: header must be aligned with either the SPF domain or the DKIM domain. This is required to pass DMARC alignment.
- Marketing messages and subscribed messages must support one-click unsubscribe, include a clearly visible unsubscribe link in the message body and process recipient unsubscribe requests within 2 days.
- Reference this for the full list.
Sender Authentication
In this section e discuss Email Authentication and how to avoid the spam folder.
There are 3 authentication standards to help protect an organization’s email:
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) specifies the servers and domains allowed to send email for your business. This protects against spoofing and helps prevent your emails from being flagged as spam. This is added as a record on public DNS server that is used to check the source IP of the email and compares it with a DNS TXT record.
v=spf1 ip4:173.236.251.117 include:netblocks.dreamhost.com include:relay.mailchannels.net mx ~all
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), used to digitally sign every outgoing message sent from your organization. The receiving server uses this to verify that it came from your business. It is a unique key for domain that allows mail servers to verify email authenticity and resist tampering. It is a generated key that is configured on a public DNS server.
v=DKIM1; k=rsa; h=sha256; p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAmY24P6ntSL6CbVrv++vyTdgVJP4jxAEDoYbpo2vMEpOb2SDnUsiiBnd8rINyMh9BMA5whxKC/w7oqYD9dr5mvfPtkVPBSz9PqFHE2s/QsFnJlBsUJJrLFBlSXw+F95TTZyqNboANJuGCGpbg207KloAd0PZxaHjyBqj9fTfFLUCp/TrEmaMZ1E3LwqXd2jqC2mUCBcIMzIOcT68eU0b5LTlRMPL7k07BOlMGSx8Ez2wYltyDXPQc9IM8rOlMmtO92O/PkyqhyqJF+QxMSAgV6CLhtghmwbRFjvKUbkAtdCYmfRqDiPrrTCZhV7RX6+3gg7F6MPstL+KefKKToFunFQIDAQAB
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance) is an email authentication protocol designed to give domain owners the ability to protect against spoofing, phishing, email scams and other cyber threats. It instructs receiving servers on how to handle outgoing messages from your organization that don’t pass SPF or DKIM.
More specifically, DMARC standardizes how email receivers perform email authentication using the SPF and DKIM authentication mechanisms. The policy is is published in the public Domain Name System (DNS) as text TXT records and used by the receiving email server to authenticate incoming emails based on the name / value tags that are defined:
"v=DMARC1; p=reject; sp=none; fo=1; rua=mailto:[email protected]; ruf=mailto:[email protected]"
DMARC:
-
Reduces email Spoofing & Phishing: Prevents bad actors from impersonating an organization’s domain by verifying which domain the email originated from.
The domain name in the
From:field in the email header is inspected and aligned with other domains authenticated by either SPF or DKIM:From: John Doe <[email protected]> -
Improves Email Deliverability: Sets policies for how the receiving email server should deal with failures.
When emails fail DMARC authentication, the DMARC policy instructs how the receiving email server should handle emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks. The options are: Accept, Reject or Quarantine the email – ensuring senders that their legitimate emails are reaching recipients inboxes.
-
Provides Reporting & Feedback: DMARC provides a reporting mechanism for policy actions performed by the above policy.
These reports provide insights to domain owners about emails sent from their organization (even if they were sent by unauthorized parties). They can be helpful in identifying and addressing email spoofing attempts.
BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification), not part of the new Gmail or Yahoo guidelines – is an emerging standard that enables organizations to showcase their validated brand logo in authenticated emails.
BIMI improves email authentication by leveraging existing email authentication protocols to validate ownership of their corporate logos. BIMI is not an authentication method, it’s more of a visual authentication indicator and brand presentation to customers.
- Verified Brand Logo: Organizations implement a BIMI record containing a verified brand logo. Participating email clients / ESP (like Gmail or Yahoo Mail) check the BIMI record associated with an incoming email. If everything is verified, the client retrieves and displays the brand logo next to the sender’s email address.
- Reduces Phishing Attacks: The visual verification helps users distinguish legitimate emails from potential phishing attempts (e.g., bank0famerica.com vs bankofamerica.com, paypalsupport.com vs support.paypal.com, etc).
- Brand Recognition: By displaying a familiar logo, BIMI can enhance brand recognition and build trust with recipients. When a recipient sees a brand’s logo, they’re more likely to view it as legitimate. This can increase email open and click-through rates – reducing the chances of it being flagged or ignored.
BIMI example for Bank of America:

To query these reccords, you can use MxToolbox:
You can also use these native OS CLI tools to query these DNS records:
- Linux:
- BSD:
- Windows:
dig -t txt xomedia.io
dig -t txt dreamhost._domainkey.xomedia.io
dig -t txt _dmarc.xomedia.io
drill txt xomedia.io
drill txt dreamhost._domainkey.xomedia.io
drill txt _dmarc.xomedia.io
nslookup -type=txt xomedia.io
nslookup -q=txt dreamhost._domainkey.xomedia.io
nslookup -q=txt _dmarc.xomedia.io
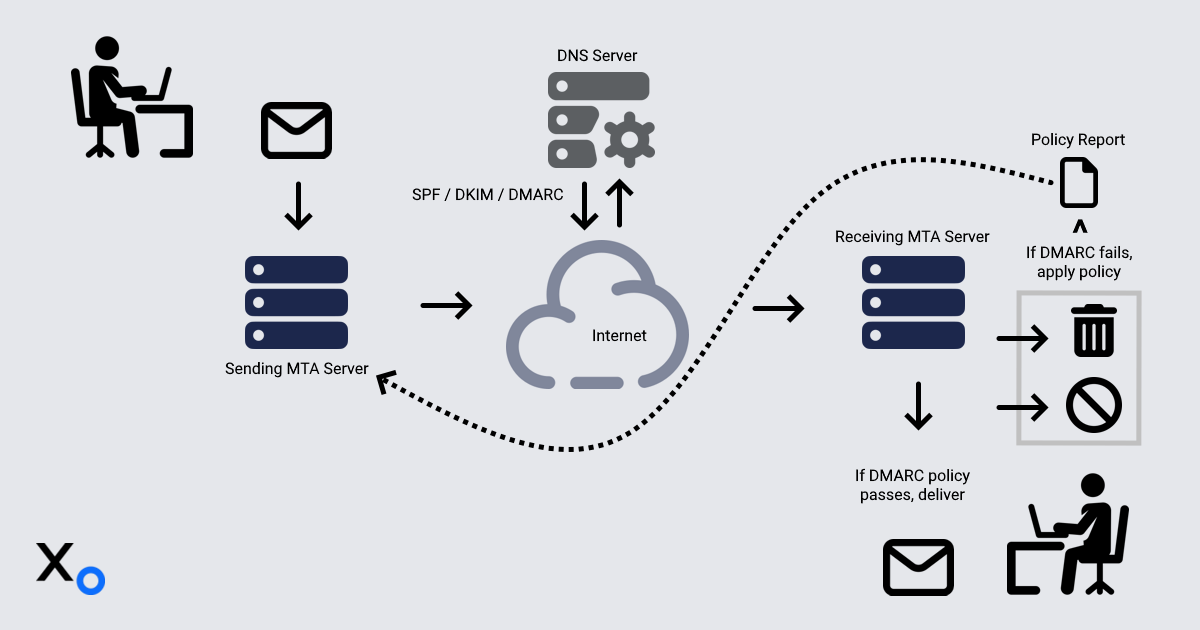
Here’s a simple diagram to help explain the entire email journey:

- Sender composes and sends an email.
- Sender’s MTA (Mail Transfer Agent on mail server) adds a DKIM signature to the email header as a special field..
- Recipient’s MTA checks SPF and DKIM records.
DMARC alignment is verified, and the policy is applied:
- If a message passes authentication by the receiving server – Deliver to user’s inbox.
If a message fails authentication by the receiving server:
Quarantine (send them to recipients’ spam folder).
NOTE: If the receiving mail server has a quarantine configured, messages might be sent to quarantine, rather than directly to the recipient’s spam folder.
Reject messages are never deliver to the recipient. The receiving server usually sends a bounce message to the sender
Here’s an example email from an organization that passes all of the email security guidelines:

Proper configuration of these standards shields against attacks and increases deliverability so that messages land in inboxes, not spam folders.
Impact
Google continuously updates its algorithms and user-reported data to improve email filtering and user experience. Google’s AI Spam filtering algorithms block 99.9% of spam, phishing and malware attempts from landing in your inbox. For 1.8 billion accounts, 15 billion unwanted emails are being blocked daily.
The following email statistics reveal the impact these new security guidelines will have on deliverability and engagement (especially for email marketing campaigns and newsletters):
- In 2025, the number of email users is expected to reach 4.6 billion (Techjury)
- In 2023, we expect to see an average of over 347 billion emails sent per day (Oberlo)
- There are projected to be an estimated 4.37 billion email users in 2023 (Statistics)
- Millennials and Gen Xers rely on their email more than any other generation at 98% (Statista)
- In 2021, an average of just over 2 hours a day are spent on email (Statista)
- 63% of people who open up an email try and find a discount (LXA)
- 99% of email users check their inbox every day, with some checking 20 times a day (HubSpot)
- The image above tells us that email marketing revenue is estimated to reach almost 12.5 billion by the end of 2024 (Statista)
- 58% of consumers check their email first thing in the morning (Optinmonster)
- 84.3% of consumers say they check their emails at least once a day (Mailjet)
Additional email stats from Sixth City Marketing
A list of the most popular email providers as of 2024 (in millions):
| Provider | Market Share | # of Users | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gmail | 29.67% | 1800 | Dominant provider, growing market share |
| Apple Mail | 22.82% | 1000 | Apple device users |
| Outlook.com | 4.3% | 500 | formerly Hotmail |
| Yahoo Mail | 2.55% | 150 | Declining market share |
| Yandex.Mail | 1.1% | 65 | Popular in Russia / Eastern Europe |
| QQ Mail | 1% | 60 | Dominant in China |
| GMX | .7% | 42 | Popular in Germany |
| AOL Mail | .6% | 36 | Declining market share |
| Zoho Mail | .3% | 18 | Business-focused provider |
| ProtonMail | .25 | 15 | Privacy-focused provider |
Sources: Oberlo, Litmus, Statista
NOTE: Countless smaller providers and self-hosted (businesses) email solutions exist. Accounting for a collective market share is difficult to accurately assess.
Tools
For convenience, here’s a curated list of free online resources to help you set up, check and maintain your organization’s email hygiene:
Google Safe Browsing site status: A free online site transparency service you can use periodically to determine if your domain has been added to their unsafe site list. Also check any other domains that are linked to yours.
SuperTool: A free online tool to verify your MX, SPF, DKIM and DMARC records. It also has a ‘Blacklist Check’ tool that allows you to verify if your email IP / Domain has been blacklisted on any of the DNS-based blacklist (DNSBL) services.
Email Health Report: A free, comprehensive online email health check that looks for DNS, domain and server issues. It also searches to see if your domain is listed on any blacklist databases. The results of this report can be used to address email related issues for your domain.
IP and Email Blacklist Check: A free online tool to determine if a domain, IP address, or email address is enlisted in the DNSBL and other blacklist databases for suspicious activity. Blacklisted addresses cannot send any emails. It’s a stricter form being blocked that requires going through an appeals process to be removed from their list.
Email Deliverability Report: Send a test email using this tool and it will: 1)Analyze the headers and blacklist reputation of your outbound IP address, 2) Verify your SPF record and 3) Email link with a comprehensive deliverability report.
DMARC Report Analyzer: This tool will make DMARC Aggregate XML reports human readable by parsing and aggregating them by IP address into readable reports.
DNS Reverse Lookup: Using the MxToolbox SuperTool again, perform an MX lookup from the domain you send emails from to determine your MX IP addresses (usually 2). Use these IPs to perform a DNS ‘Reverse Lookup’ from the MxToolbox SuperTool drop-down menu.
IP and domain reputation checker.
This is a free service that provides valuable insights and diagnostics. If you are a bulk sender (5,000 daily emails), it’s worth setting up to get valuable information about:
- When recipients mark your messages as spam.
- Why your messages might not be delivered.
- If your messages are authenticated.
- Your domain or IP reputation and its impact on message delivery rates.
Implementation
Implementing these guidelines will no doubt pose challenges for smaller organizations with limited resources. As mentioned earlier, many companies faced similar challenges transitioning to HTTPS for the Web, and MFA for online accounts. Email compliance is now rapidly becoming a mandatory standard that every business must become familiar with.
While these efforts may seem daunting, it’s important to understand that adapting to stricter security guidelines brings significant benefits such as stronger email security, customer trust and ensures that your emails are reaching their inboxes. Prioritizing these measures will elevate your brand and pave the way for business success.
To implement email authentication, consult with your service provider’s resources or support. For example, here’s collection of resource links for some well-known service providers:
Adoption is an important first step, being vigilant in the face of evolving security threats is equally important. Businesses will also need to be diligent about keeping up with changing standards.
By leveraging automation, organizations can effortlessly keep pace with shifting standards – ensuring continuous compliance:
- Continuously monitor email provider documentation for policy updates.
- Query and perform DNS record verification and validation.
- Analyze DMARC reports (both aggregate and forensic) for anomalies based on defined keywords.
- Configure an email alert to notify you of any events triggered from the above steps.
Bonus
In this section we’re going to show you a couple of methods hackers employ to exploit email security loopholes. Failing to secure email systems properly exposes your customers to malicious actors who can hijack email domains for nefarious purposes.
Email Spoofing and Phishing are two tactics commonly used to trick recipients:
Spoofing (impersonating): Involves sending emails that appear to be from a legitimate sender, like a bank, a company or even a friend. The goal is to trick the recipient into clicking on a malicious link, opening an infected attachment or revealing personal information. Spoofing is often used in phishing emails that aim to extract personal data from recipients.
Phishing (action): Is a type of cyberattack that uses deceptive emails to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, clicking on malicious links or downloading infected attachments. The attackers typically impersonate legitimate organizations or individuals to gain the recipient’s trust and make the email appear believable.
The following command line mail utilities are commonly used in scripts to change email header information such as “From:”, “To:” and “Subject:”.
A hacker will also go to great lengths setting up a remote web server with a login page that looks like the login page of a banking institution or social media platform.
These commands are automated using scripts (small programs) that are easily adaptable to impersonate an email from your bank with a link to a fake login page to fool you into entering login credentials. These attacks can be very persistent, crafty and intelligently designed to evade both human and spam detection measures.
The mail / mailx utility:
cat login.php | mail -s "$(echo -e "Test\nContent-Type: text/html")" [email protected] -- -f [email protected]echo "email body" | mailx -s "An email subject" [email protected] -a "From: [email protected]"mutt -H - "$2" <<EOF
From: $1
To: $2
Subject: $3
Importance: high
$4
EOF
Summary
In this article we covered:
- The new mandatory guidelines and best practices that email providers are enforcing in 2024 and the impact it will have on businesses.
- We explained how to implement these guidelines and how to remain compliant.
- We also provided some free online tools to help with implementation and compliance.
Bulk senders are required to authenticate emails, be careful not exceed spam rate thresholds and implement one-click unsubscribes for email marketing campaigns and newsletters.
As email service providers enforce stricter guidelines, organizations need to be proactive with compliance. While implementing these guidelines can be complex, the benefits will be well worth it. Not only will it enhance security, it will boost email deliverability and engagement rates. Ultimately this will drive more sales and revenue, helping you stand out in a crowded digital marketplace.
Just as many companies faced similar challenges transitioning to HTTPS and MFA, email compliance is rapidly becoming a standard that every business must become familiar with. These security benefits will elevate your brand and pave the way for business success by building customer trust and ensuring emails reach their inboxes.
References
Email sender guidelines FAQ
Google BIMI Support
New Gmail protections for a safer, less spammy inbox
Understanding Gmail’s spam filters
Spam does not bring us joy—ridding Gmail of 100 million more spam messages with TensorFlow
Yahoo
Sender Requirements & RecommendationsYahoo BIMI Support
Postmaster @ Yahoo & AOL
Yahoo Mail Blog
One-Tap Unsubscribe
Email Sender Support
Outlook.com (formerly Hotmail)
Sender guidelinesMicrosoft BIMI Support
SPF/DKIM/DMARC/BIMI Orgs
open-spf.orgdkim.org
dmarc.org
bimigroup.org
RFCs
SPF RFC 7208
DKIM RFC 6376
DMARC RFC 7489
One-Click Unsubscribe RFC 8058
BIMI RFC Draft
Internet Message Format RFC 5322
SMTP RFC 5321
Mailing Lists RFC 2369
Important: Sending ‘unsolicited email’, or ‘cold emailing’ are governed by various laws and regulations depending on your target audience and location:
- CAN-SPAM Act (USA): This law governs commercial email marketing in the United States. It outlines requirements for subject lines, sender identification, unsubscribe options, and more. Compliance is mandatory.
- GDPR (EU): Applies to processing personal data of individuals within the European Union. Requires explicit consent for marketing emails unless you have a legitimate business relationship with the recipient.
- CASL (Canada): Canadian Anti-Spam Legislation imposes similar requirements to CAN-SPAM, including opt-in consent and unsubscribe options.
- Many other countries have specific laws governing unsolicited email. Always do your homework before sending emails internationally.
Thanks for Reading!
XOMedia is a full-service IT solutions provider. Learn how your business can benefit from XOMedia's 30+ years of experience with our Consulting and Partnership services - all work is backed by our 100% guaranteed.
Back to Blog Home